Characteristics of Various Types of Gearboxes
Technical Information for Motor-Gearbox Combinations, ①, Characteristics of Various Types of Gearboxes
Spur gearbox
1、The torque is relatively low, but can be thin and quiet design.
2、Efficiency,91% per stage
3、nput and output shafts can be coaxial or parallel offset
4、Input, output of the rotation direction due to different gear levels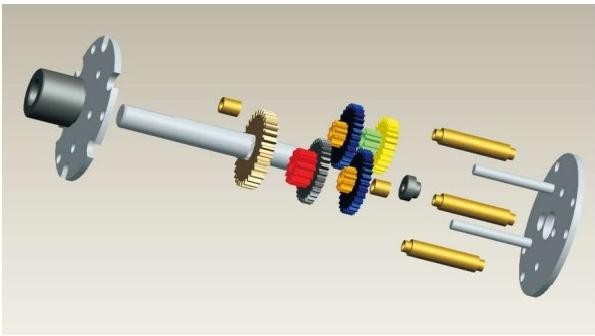
Planetary gearbox
1、Capable of high torque transmission and high torque density
2、Efficiency,79% per stage
3、The location of input and output: the same center
4、Input, output rotation in the same direction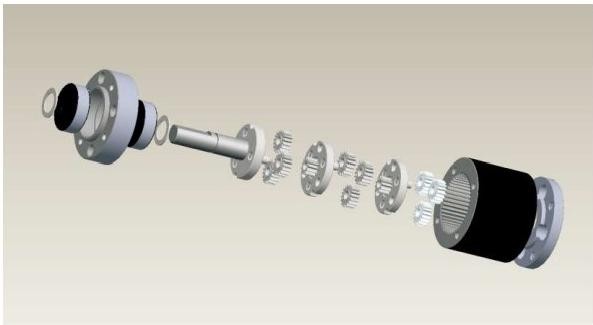
Gear efficiency
Gearboxes have some mechanical loss (gearengagement and bearing friction, etc.). In general, each level of gear occlusion, in accordance with the planetary gear reducer 79%, spur gear reducer efficiency of 90% to calculate efficiency. The per-stage efficiencies provided are typical peak values under rated conditions. Actual efficiency varies significantly with load, speed, and temperature, and will be substantially lower under low-torque conditions. Therefore, only as areference value. In the low torque state when used, the efficiency will be greatly reduced
- An example of calculation of efficiency:
Spur gear 5-stage meshing
Efficiency(η)= 0.91×0.91×0.91×0.91×0.91≈0.624(62.4%)
planetary gear 3-stage meshing
Efficiency(η)= 0.79×0.79×0.79≈0.493(49.3%)
- The relationship of speed and torque between gearbox and motor

gearbox output torque=Ts×gear ratio×η
Example:
Gearbox Output torque N0: 14800RPM ,Stall torque Ts=15g.cm, with 100:1,gearbox transmission efficiency:60%
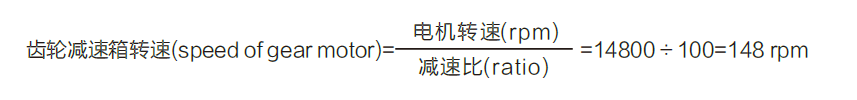
gearbox output torque=Ts×gear ratio×η=15×100×60%=900 g.cm
- The effect of number of gear stages on motor rotation
When the number of spur gear stages is odd, the direction of rotation of the gearbox output shaft is opposite to that of the motor output shaft.
When the number of spur gear stages is even, the gearbox output shaft rotates in the same direction as the motor output shaft.
The rotation direction of the planetary gearbox output shaft is the same as the rotation direction of the motor output shaft, regardless of the number of stages.





