Guide to DC Motor Technical Parameters
Technical Information for Motor-Gearbox Combinations, ③, Guide to DC Motor Technical Parameters
- The following values are measured and calculated at nominal voltage under the temperature at 25 ℃
1、Technical words
| Words | Symbol | Unit | 用 语 | Symbol | Unit |
| Voltage | U | V | Input power | P | W |
| Current | I | A | Output power | P | W |
| No-load current | I0 | A | Maximum output power | Pmax | W |
| Stall current | Is | A | Efficiency | η | % |
| Speed | N | r/m,rpm | Maximum efficiency | ηmax | % |
| No-load speed | N0 | r/m,rpm | Torque | T | g.cm,mN.m |
| Resistance | R | Ω | Stall torque | Ts | g.cm,mN.m |
2、No load current--I0
The current consumed after stable under the rated voltage when there is no loaded. This parameter will be affected by different temperatures.
3、No load speed--N0
The highest speed obtained after stable under the rated voltage.
4、Stall torque--Ts
Stall Torque is the torque produced by the motor whose output rotation speed is zero under the rated voltage. This parameter is highly effected by different temperatures.) step-by-step: 1. Basic relation: . 2. Stall current: . 3. Predictive model with friction:
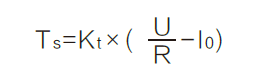
5、Stall current--Is
Stall current is the current that the motor draws when its shaft if prevented from moving.

6、Maximum output power--Pmax
The maximum output power of the motor at the rated voltage.
7、Maximum output efficiency--ηmax
The maximum ratio of output power of the motor to the consumption of electrical power.
8、Back - EMF Constant--KE(mV/rpm)
The constant corresponding to the relationship between the induced voltage in the rotor and the speed of rotation.
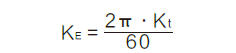
9、Torque constant--Kt (g.cm/A)
The constant corresponding to the relationship between the torque developed by the motor and the current drawn.) In SI units, the Torque Constant () and the Back-EMF Constant () are numerically equal.
10、Speed constant--Kn (rpm/V)
The speed variation per volt applied to the motor terminals at the constant load.
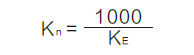
11、Mechanical time constant--tm (ms)
The time required for the motor to reach a speed of 63% of its final no load speed, from standstil.
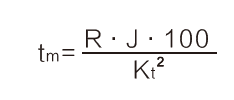 , R: (Static resistance), J: (Rotor inertia)
, R: (Static resistance), J: (Rotor inertia)





